Health & Medicine
Prolonged And Recurring Jet Lag Connected To Elevated Risks Of Liver Cancer
Savitha .C.Muppala
First Posted: Nov 28, 2016 03:15 AM EST
First Posted: Nov 28, 2016 03:15 AM EST
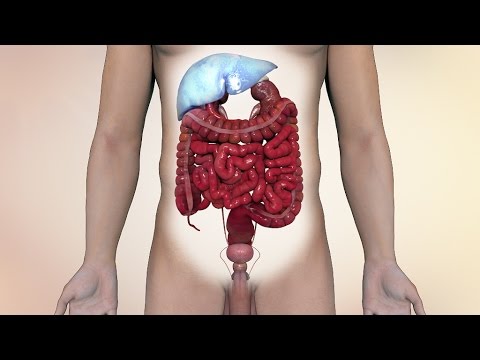
A recent study by researchers from Baylor College of Medicine (BCM) has found that those experiencing chronic jet lag could be exposing themselves to elevated risks of liver disease and cancer. Obesity is the major fallout of those under the throes of prolonged jet lag.
Erratic Sleep Timings And Cancer Risk
The study found that too many alterations in sleep timings as well as exposure to light could trigger the abnormal production of bile acids. This can increase risk of cancer, the study revealed.
According to David Moore, team leader of the research team, the link between those suffering fatty liver disease and liver cancer cannot be ignored. He also said that statistics have shown the growing incidence of liver cancer worldwide. Victims of fatty liver disease could go on to develop liver cancer even without coming down with cirrhosis, he said.
Experiments On Mice
The research team from BCM conducted a study on mice that were jet lagged. They found that mice experiencing prolonged and recurrent jet lag went on to develop liver cancer. This pattern showed a close similarity to humans.
Explaining the connection, Moore said that when a person is exposed to light, the central circadian clock of the brain resets. NDTV explains that when a person is awake at odd hours, has an erratic sleep pattern or travels extensively across time zones, this clock gets disturbed.
The disturbance to the circadian clock negatively impacts body metabolism. Tests on jet lagged mice on a healthy diet appeared to gain weight and went on to develop fatty liver disease. This later progressed to liver cancer, reveals Tech Times.
Jet Lag And Cancer
When the circadian clock gets disturbed, experiments on mice revealed that two receptors get triggered or stimulated to set right metabolism in the body. FXR receptor that controls the production of bile acids in liver was malfunctioning in jet lagged mice. This led to the production of abnormal levels of bile acids that led to liver cancer, the experiments found.
The same receptors are found in humans, too. Therefore, chronic jet lag could result in liver cancer, concluded researchers in the study published in the Journal Cancer Cell.
See Now: NASA's Juno Spacecraft's Rendezvous With Jupiter's Mammoth Cyclone